
Cataract surgery has undergone remarkable advancements, offering patients a variety of intraocular lens (IOL) options to restore vision. Among these, multifocal lenses have emerged as a popular choice for individuals aiming to reduce their dependence on glasses post-surgery. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of multifocal IOLs, including their design, benefits, potential drawbacks, and considerations for patients contemplating this option.
Multifocal intraocular lenses are artificial lenses implanted in the eye to replace the natural lens affected by cataracts. Unlike traditional monofocal lenses, which focus at a single distance (usually for clear distance vision), multifocal IOLs are engineered to provide clear vision at multiple distances—typically near, intermediate, and far. This multifocality aims to mimic the eye's natural accommodative ability, which often diminishes with age.
Design and Functionality
Multifocal intraocular lenses (IOLs) are meticulously engineered to distribute light across multiple focal points, facilitating clear vision at various distances. This multifocality is achieved through distinct lens designs, each employing unique optical principles to address specific visual requirements:
Diffractive Lenses
Diffractive multifocal IOLs utilize a series of concentric rings etched onto the lens surface. These rings create step-like structures that diffract incoming light, splitting it into distinct focal points corresponding to near, intermediate, and distance vision. A notable advantage of diffractive lenses is their relative independence from pupil size; they maintain consistent performance under varying lighting conditions, providing reliable multifocality regardless of whether the pupil is dilated or constricted. However, the diffraction process can lead to some light loss and may introduce visual phenomena such as halos or glare, especially in low-light environments.
Refractive Lenses
Refractive multifocal IOLs employ zones with differing refractive powers arranged in specific patterns across the lens surface. Each zone is tailored to focus light at a particular distance, enabling the eye to switch focus between near, intermediate, and far objects. The effectiveness of refractive lenses is influenced by pupil size; certain zones are activated depending on lighting conditions, which can affect the quality of vision at different distances. Proper centration of the lens is crucial to ensure optimal performance, as misalignment can lead to visual disturbances.
Hybrid Lenses
Hybrid multifocal IOLs integrate both diffractive and refractive elements to leverage the strengths of each design while mitigating their individual limitations. By combining diffractive rings with refractive zones, these lenses aim to provide a seamless transition between focal points, enhancing visual quality across various distances. The hybrid approach seeks to balance the pupil independence of diffractive designs with the smooth focal transitions of refractive designs, offering patients a more versatile visual experience.
Extended Depth of Focus (EDOF) Lenses
Extended Depth of Focus lenses represent an innovative category in multifocal IOL design. Instead of creating multiple distinct focal points, EDOF lenses elongate the focus range to provide a continuous zone of clear vision, particularly enhancing intermediate vision without compromising distance vision. This design minimizes the overlapping of out-of-focus images, reducing the likelihood of visual disturbances such as halos and glare. However, near vision may still require the use of reading glasses, depending on the individual's specific visual needs.
Segmented and Aspheric Multifocal Lenses
Some multifocal IOLs feature segmented designs, where distinct lens segments are dedicated to different focal lengths. This segmentation can improve contrast sensitivity and reduce visual disturbances by minimizing the overlap between focal zones. Aspheric multifocal lenses incorporate aspheric surfaces to counteract spherical aberrations, enhancing image quality and providing sharper vision across all distances.
In summary, the design and functionality of multifocal IOLs are pivotal in determining their performance and suitability for individual patients. Understanding the nuances of each design aids in selecting the most appropriate lens type, aligning with the patient's visual requirements and lifestyle preferences.

Multifocal intraocular lenses (IOLs) offer several advantages for patients undergoing cataract surgery, aiming to enhance visual acuity across various distances and improve overall quality of life:
Reduced Dependence on Glasses
One of the primary benefits of multifocal IOLs is the significant reduction in reliance on corrective eyewear. These lenses are designed to provide clear vision at multiple distances—near, intermediate, and far—enabling patients to perform daily activities such as reading, computer work, and driving without the constant need for glasses. This increased visual independence can lead to greater convenience and satisfaction in everyday life.
Enhanced Quality of Life
By offering a broader range of clear vision, multifocal IOLs contribute to an improved quality of life. Patients often experience greater freedom in their daily routines, engaging in various tasks and hobbies without the hindrance of switching between different pairs of glasses. This enhancement in visual function can lead to increased confidence and participation in social and recreational activities.
Cost Savings Over Time
While the initial investment in multifocal IOLs may be higher compared to monofocal lenses, patients may experience cost savings over time. The reduced need for multiple pairs of prescription glasses—such as those for reading, computer use, and distance vision—can result in decreased expenses related to eyewear purchases and maintenance.
Convenience and Aesthetics
Eliminating or reducing the need for glasses offers practical benefits, such as convenience and aesthetic preferences. Patients can enjoy activities like swimming, exercising, or participating in sports without the concern of managing corrective eyewear. Additionally, some individuals prefer the natural appearance of being glasses-free, which can positively impact self-esteem and confidence.
Improved Binocular Vision
Multifocal IOLs can enhance binocular vision by providing balanced visual input from both eyes across various distances. This improvement supports better depth perception and coordination, which are essential for tasks like driving, navigating stairs, and engaging in sports or other activities that require precise spatial judgment.
Potential Reduction in Presbyopia Symptoms
Presbyopia, the age-related loss of near focusing ability, is a common concern among individuals over 40. Multifocal IOLs address this issue by incorporating multiple focal points, thereby reducing or eliminating the need for reading glasses. This feature allows patients to enjoy clear near vision, enhancing their ability to read fine print, use mobile devices, and perform other close-up tasks comfortably.
In summary, multifocal IOLs provide numerous benefits that extend beyond mere vision correction. They offer a comprehensive solution that enhances visual independence, quality of life, and overall satisfaction for patients undergoing cataract surgery.
While multifocal intraocular lenses (IOLs) offer significant benefits, they are associated with certain challenges that patients should consider:
Visual Disturbances
Some individuals experience visual disturbances after receiving multifocal IOLs. These may include:
Adaptation Period
Adjusting to multifocal IOLs requires time:
Cost Considerations
Financial aspects are an important consideration:
Other Considerations
Additional factors to keep in mind include:
In summary, while multifocal IOLs can reduce dependence on corrective eyewear and improve quality of life, potential drawbacks such as visual disturbances, adaptation periods, and higher costs should be considered. A detailed discussion with your cataract surgeon can help you determine the most suitable option based on individual needs and expectations.
Not all patients are ideal candidates for multifocal intraocular lenses (IOLs). A thorough preoperative evaluation is essential to determine suitability. Factors influencing candidacy include:
Lifestyle Needs
Understanding a patient's daily activities and visual requirements is crucial. Individuals who engage in tasks demanding sharp vision, such as night driving or detailed close-up work, should discuss these needs with their ophthalmologist. For example, professions like pilots or surgeons, where precise vision is imperative, may require careful consideration before opting for multifocal IOLs. Conversely, patients seeking reduced dependence on glasses for everyday tasks may find multifocal IOLs beneficial.
Ocular Health
Pre-existing eye conditions can significantly impact the performance of multifocal lenses. Conditions such as macular degeneration, glaucoma, or significant astigmatism may contraindicate their use. A comprehensive eye examination is necessary to assess the overall health of the eye, including the cornea, retina, and optic nerve. Identifying issues like dry eye syndrome or corneal irregularities is essential, as these can affect postoperative outcomes.
Expectations
Setting realistic expectations is vital for patient satisfaction. Patients should understand that while multifocal IOLs aim to reduce dependence on glasses, they may not eliminate the need entirely. There is also the potential for visual disturbances, such as glare or halos, especially in low-light conditions. A thorough discussion with the ophthalmologist about the benefits and limitations of multifocal IOLs can help align expectations with likely outcomes.
Personality and Adaptability
A patient's personality and adaptability play a role in the success of multifocal IOL implantation. Individuals who are meticulous or have perfectionist tendencies may be more sensitive to minor visual imperfections and, therefore, less satisfied with the results. Conversely, patients with a flexible attitude and a positive outlook are more likely to adapt successfully to the visual changes associated with multifocal IOLs.
Age and Neuroadaptation
Younger patients may have a higher capacity for neuroadaptation, adjusting more readily to the visual changes introduced by multifocal IOLs. However, they may also have higher visual demands and expectations. Older patients, while potentially having lower expectations, might experience a longer adaptation period. Discussing these aspects can help tailor the choice of IOL to the patient's age-related adaptability.
Corneal Astigmatism
The presence and degree of corneal astigmatism are critical considerations. Patients with significant astigmatism may require additional procedures, such as limbal relaxing incisions or toric IOLs, to achieve optimal visual outcomes. Accurate measurement and correction of astigmatism are essential to ensure the effectiveness of multifocal IOLs.
Pupil Size and Dynamics
Pupil size can influence the performance of multifocal IOLs, particularly in low-light conditions. Patients with larger pupils may experience more pronounced visual phenomena, such as halos or glare, due to increased light entering through peripheral zones of the lens. Assessing pupil dynamics under various lighting conditions can aid in selecting the most appropriate IOL design.
Occupational Considerations
Certain occupations may be less compatible with the visual characteristics of multifocal IOLs. For instance, individuals whose work involves detailed visual tasks in low-light environments, such as astronomers or night-time truck drivers, may find the potential visual disturbances unacceptable. A detailed occupational history helps in making an informed decision.
Psychological Factors
Patients' psychological profiles, including their ability to handle potential postoperative visual disturbances, are important. Those with anxiety disorders or unrealistic expectations may require additional counseling or may be better suited to alternative vision correction options.
In conclusion, selecting suitable candidates for multifocal IOLs involves a comprehensive evaluation of various factors, including lifestyle, ocular health, expectations, and psychological readiness. A personalized approach ensures that the benefits of multifocal IOLs align with the patient's unique visual needs and lifestyle, leading to higher satisfaction and optimal visual outcomes.
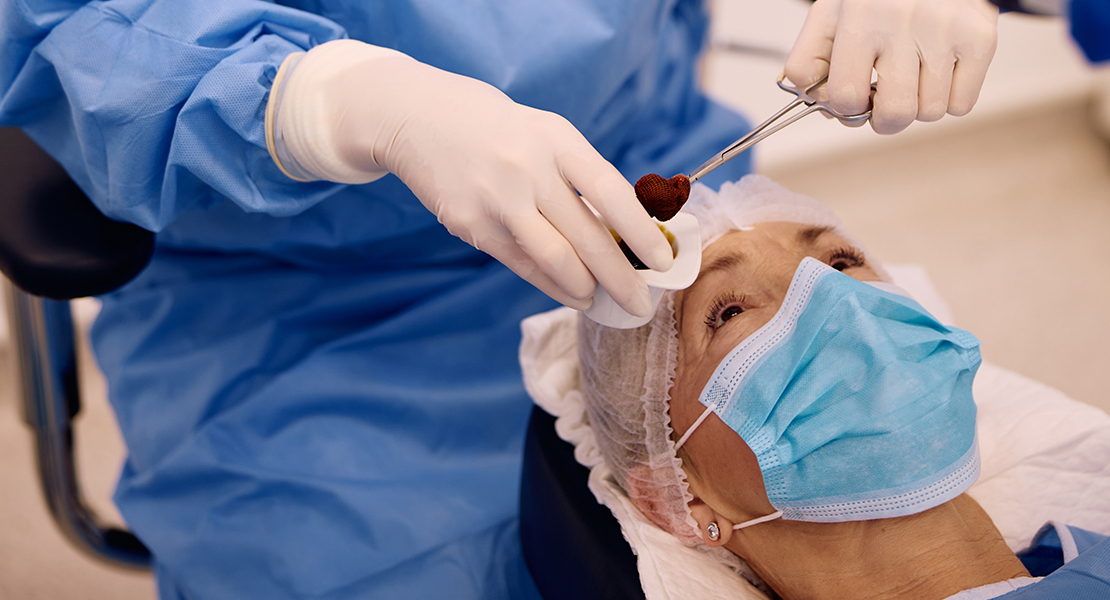
The implantation of a multifocal intraocular lens (IOL) during cataract surgery involves several precise steps to ensure optimal visual outcomes:
After the surgery, diligent postoperative care is essential to facilitate healing and achieve the best possible visual outcomes:
Adhering to the postoperative care instructions provided by the ophthalmologist is vital for a smooth recovery and the successful integration of the multifocal IOL, leading to enhanced visual acuity across various distances.
To learn more about the surgical procedure, explore the additional articles available in our Resources section and blog.
Multifocal intraocular lenses represent a significant advancement in cataract surgery, offering patients the possibility of clear vision at multiple distances and reducing reliance on glasses. However, the decision to opt for multifocal IOLs should be made after a comprehensive evaluation and discussion with an experienced ophthalmologist, considering individual visual needs, lifestyle, and potential risks. Informed decision-making ensures that patients achieve the best possible outcomes tailored to their unique circumstances.