When you’re preparing for cataract surgery, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is choosing the right lens. If you have even a small amount of astigmatism, your surgeon may recommend a toric intraocular lens (IOL). But if your astigmatism is only mild, you may wonder whether a toric lens is really necessary or whether a standard lens will be “good enough.”
The truth is that mild astigmatism affects people differently. Some barely notice it, while others experience blur, ghosting, or uneven clarity that affects their day-to-day vision. When you combine this with your goals for life after cataract surgery especially if you hope to reduce your reliance on glasses the importance of correcting even small astigmatism becomes clearer.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through how mild astigmatism actually affects your vision, how surgeons decide whether toric lenses are worthwhile, and the situations where a standard lens may still be enough. My goal is to give you a complete picture so you can make a confident decision about your surgery.
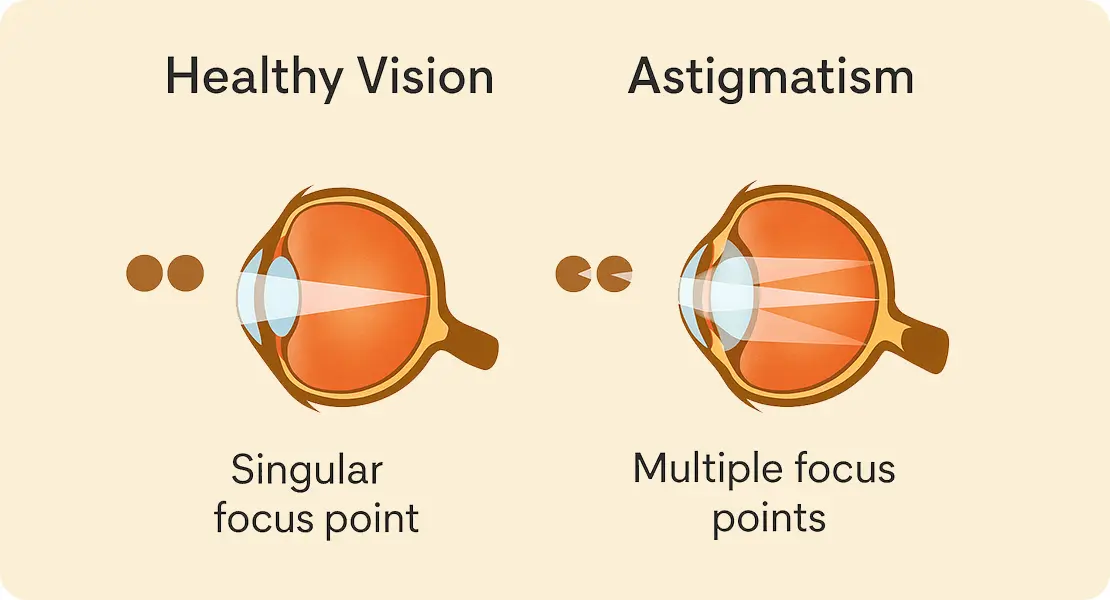
What Mild Astigmatism Really Means
Astigmatism isn’t a disease it’s simply a difference in the curvature of your cornea. Instead of being evenly rounded, the surface is slightly oval, which causes light to focus unevenly on the retina.
Because of this uneven focus, you may notice subtle visual symptoms such as slight blur, shadowing around letters, or uneven clarity. These effects are often more noticeable in low light or while driving at night. Mild astigmatism usually falls between 0.50D and 1.00D, sometimes a little higher. While these numbers may seem small, even minor irregularities can affect sharpness inside the eye especially after eye surgery.
Many people assume mild astigmatism isn’t worth correcting. However, after cataract removal, the eye becomes much clearer, making any remaining blur stand out more than before, which is why mild astigmatism often feels more noticeable post-surgery.
Why Mild Astigmatism Matters After Cataract Surgery
Many people cope well with mild astigmatism before surgery because their eyes and brain gradually adapt over time. However, after cataract surgery, visual expectations naturally increase most patients want the clearest, sharpest vision possible from their new intraocular lens.
This is why even low levels of astigmatism matter after surgery:
1. Cataracts mask small imperfections: A cloudy natural lens softens vision and blurs fine detail, which can hide minor refractive errors. Once it is replaced with a clear IOL, any remaining astigmatism often becomes more noticeable.
2. Surgery resets your visual system: Cataract surgery usually delivers a dramatic improvement in clarity and brightness. If mild astigmatism remains, it can feel like an avoidable compromise rather than a true limitation.
3. Astigmatism affects both distance and near vision: Even small amounts can reduce sharpness at all distances. This may be noticed when reading road signs, using digital screens, or performing close work.
4. You may become more aware of night-time visual issues: Uncorrected astigmatism can cause halos, streaks, or smearing of lights. These effects are often more noticeable in low-light conditions such as night driving.
5. Glasses independence may be harder to achieve :If your goal is to reduce reliance on glasses, even mild astigmatism can prevent fully spectacle-free vision. Correcting it improves the likelihood of clear vision without additional optical aids.
All of these factors are why surgeons carefully measure and account for even small amounts of astigmatism when planning cataract surgery and selecting the most appropriate lens option.
How Surgeons Decide Whether Toric Lenses Are Worth It
Choosing a toric lens for mild astigmatism is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Surgeons consider several factors together to decide whether the additional correction will provide meaningful benefit for you.
1. Your visual priorities: If your goal is the clearest possible distance vision without relying on glasses, a toric lens is often recommended, even for low levels of astigmatism. If you are comfortable wearing glasses most of the time, a standard monofocal lens may be sufficient.
2. Your lifestyle: People who drive frequently particularly at night tend to notice even mild astigmatism more clearly. Those who spend long hours on computers, reading, or doing detailed work may also benefit from sharper, more consistent clarity.
3. Your corneal measurements: Surgeons carefully assess several technical factors when evaluating astigmatism, including corneal curvature, the axis of astigmatism, the degree of irregularity, and posterior corneal astigmatism.
4. The symmetry between your two eyes: Even if only one eye has mild astigmatism, balancing both eyes for similar clarity can significantly improve visual comfort and reduce strain. This symmetry often leads to better overall satisfaction after surgery.
5. Your goals for glasses after surgery: If you are aiming for full or near-complete glasses independence, toric lenses are usually the more effective choice. They reduce the likelihood of needing spectacles for distance vision post-operatively.
6. Your eye anatomy: Some eyes are more suitable for toric correction due to their shape and stability. Your surgeon will explain whether your anatomy supports predictable toric lens performance.
This personalised assessment ensures that the lens recommendation aligns closely with your visual expectations, lifestyle needs, and long-term satisfaction.
How Much Mild Astigmatism Affects Your Vision
It’s easy to underestimate how much even small amounts of astigmatism can affect vision. For example, 0.50D of astigmatism is minor but still noticeable for people seeking sharp, unaided distance vision.
With 0.75D of astigmatism, you may notice shadowing or slight distortion, particularly when reading road signs or distant text. These subtle effects can make everyday tasks feel less clear.
At 1.00D of astigmatism, most patients experience enough blur or distortion that they appreciate correction. Vision clarity is noticeably improved when this level is addressed.
When astigmatism reaches 1.25D or higher, toric correction is usually recommended unless there’s a specific reason not to. Even mild astigmatism can reduce the crispness and precision that many patients expect after cataract surgery.
When a Standard Lens May Still Be Enough
Not every patient with astigmatism automatically needs a toric lens. In some cases, a standard monofocal lens can still provide excellent vision, depending on your lifestyle, eye measurements, and personal preferences. Here are the main situations where a standard lens may be enough.
1. You don’t mind wearing glasses – If your plan is to wear glasses for most vision tasks, correcting mild astigmatism surgically may not be essential.
2. You prefer simplicity – Some people choose to keep things straightforward, even if it means needing glasses after surgery.
3. Your astigmatism is borderline – If astigmatism is around 0.25–0.50D (depending on other measurements), surgeons may leave it uncorrected.
4. You have certain types of corneal irregularity – Some eyes don’t benefit much from toric correction because the astigmatism isn’t regular enough.
5. Cost considerations – Toric lenses are premium lenses. While many people find the investment worthwhile, it’s important to choose based on your priorities.
6. You plan monovision – If one eye is set for distance and the other for near vision, mild astigmatism may be less impactful in some cases.
In these situations, a standard lens may still deliver a very good visual outcome.
The Advantages of Toric Lenses for Mild Astigmatism
The main advantage of toric lenses is improved visual clarity, particularly for those who want to reduce their dependence on glasses. Even mild astigmatism can cause subtle blur that toric lenses correct effectively.
Many patients notice sharper distance vision and less blur or ghosting after choosing a toric lens. These improvements make everyday tasks like reading signs or watching TV feel clearer.
Toric lenses also enhance contrast and make night driving more comfortable. Reduced halos and ghosting can significantly improve safety and confidence after dark.
Other benefits include better screen clarity and more stable focus throughout the day. While each improvement may seem small alone, together they create a noticeably cleaner, more comfortable visual experience.
How Precise Modern Toric Lenses Are
Modern toric IOLs are highly advanced and designed for precision. They are engineered to stay stable within the eye, resist rotation, and provide predictable visual outcomes.
These lenses feature improved haptic design, which helps the support arms hold the lens securely in place. This ensures the lens maintains its correct orientation for optimal vision.
Material advancements also improve adhesion and surface friction, reducing the risk of lens movement over time. Greater stability in the capsular bag contributes to consistent results after surgery.
During surgery, high-accuracy alignment tools allow surgeons to position toric lenses precisely. This combination of advanced lens design and precise techniques is why patients often choose premium options, such as toric lenses in London, even for mild astigmatism.
How Toric Lenses Compare With Glasses and Laser Enhancements
If astigmatism isn’t corrected during cataract surgery, many patients still need glasses afterward. Even mild astigmatism can make distance vision slightly blurry or cause subtle distortions.
Some people with mild astigmatism may eventually explore other options, such as glasses, contact lenses, or laser eye enhancement. Each approach can improve vision, but they require ongoing management.
Using a toric lens during surgery addresses the astigmatism directly, providing a long-term solution. This reduces or eliminates the need for additional corrective measures later.
For patients who value glasses independence, toric lenses are often the most efficient and predictable way to achieve clear, stable vision. Correcting astigmatism at the time of cataract surgery can save time, cost, and hassle in the long run.
What Happens If Mild Astigmatism Is Left Uncorrected?
Even if a standard lens is used, cataract surgery will still remove the cloudy natural lens and improve overall clarity. However, some patients may notice lingering effects caused by uncorrected astigmatism:
- Residual blur: Vision may not feel completely sharp, particularly when focusing on distant objects.
- Difficulty with fine detail: Reading small print, working on a computer, or doing detailed craft tasks can remain slightly challenging.
- Shadowing around letters: Mild astigmatism can create ghosting or shadow effects when reading, reducing visual comfort.
- Less crisp distance vision: Objects at a distance may appear slightly softer than expected, even after cataract removal.
- More dependence on glasses: You may need spectacles for certain activities such as driving, watching TV, or outdoor tasks.
- Discomfort with night driving: Lights from oncoming cars or street lamps can appear streaked or haloed, making night-time vision less comfortable.
While these effects don’t occur for everyone, they are common enough that surgeons increasingly recommend toric lenses even for mild astigmatism, to provide the sharpest, clearest vision possible after surgery.
How Surgeons Personalise the Recommendation
Deciding whether a toric lens is right isn’t based on a single measurement. Surgeons consider multiple factors, including corneal power, astigmatism axis, and posterior corneal curvature.
Other aspects of your eyes also matter, such as pupil behaviour, overall eye symmetry, and specific clinical measurements. These help predict how the lens will perform in real life.
Lifestyle and personal goals are equally important. A patient’s daily activities, work needs, and vision expectations all influence the recommendation.
Age and long-term expectations are also taken into account. This is why a personalised examination is essential two people with the same measurements might receive very different advice based on their unique circumstances.
How Toric Lenses Fit into Your Overall Cataract Strategy
Cataract surgery provides a unique opportunity to optimise your vision, because you typically won’t get a second chance to choose your lens. Many patients use this moment to select the option that maximises clarity for decades.
Toric lenses can be an important part of a broader cataract strategy. They specifically correct astigmatism while working alongside other vision goals. Options may include both-eye distance correction, blended vision, or monovision setups. Some patients also consider enhanced intermediate vision arrangements depending on their lifestyle needs.
Your surgeon will guide you in choosing the approach that best matches your daily activities and long-term vision goals. This personalised plan ensures the clearest and most functional outcome possible.
Are Toric Lenses Worth It Financially for Mild Astigmatism?
Many patients with mild astigmatism find toric lenses to be a worthwhile investment. The improvement in vision is often noticeable and provides clear daily benefits.
Toric lenses can enhance clarity, comfort, and reduce reliance on glasses. They also improve confidence, especially during night driving.
For those who prioritise these advantages, the additional cost is generally justified. It’s an investment in long-term visual quality and convenience.
However, if glasses don’t bother you or your priorities are different, a standard lens may still provide excellent results. Ultimately, the choice depends on aligning your lifestyle and vision goals with the available technology.
FAQs:
1. What is a toric lens, and how does it differ from a standard lens?
A toric lens is a type of intraocular lens designed to correct astigmatism in addition to regular vision needs, such as distance or near focus. Unlike standard monofocal lenses, which only correct for one focal point, toric lenses have a specific curvature that counteracts the irregular shape of the cornea, providing clearer and more consistent vision. This makes them particularly beneficial for patients with even mild astigmatism who wish to reduce their dependence on glasses.
2. How do surgeons determine if I need a toric lens?
Surgeons consider several factors before recommending a toric lens. They measure the degree and axis of astigmatism, assess the cornea’s overall curvature, and examine posterior corneal astigmatism. They also take into account your visual priorities, lifestyle, and goals for glasses independence. By combining these measurements with personal preferences, they can predict whether the additional correction will significantly improve your vision after surgery.
3. Can mild astigmatism significantly affect vision after cataract surgery?
Yes, even small amounts of astigmatism can be noticeable once cataracts are removed. Cataracts naturally blur vision, masking minor irregularities. After surgery, your eyes experience sharper clarity, making previously subtle distortions more obvious. Mild astigmatism can lead to slight blur, shadowing, or uneven focus, which may impact tasks like reading road signs, using screens, or night driving.
4. Are toric lenses suitable for everyone with mild astigmatism?
Not necessarily. While toric lenses are effective, suitability depends on the eye’s anatomy, the regularity of astigmatism, and the degree of correction needed. Some patients may have irregular corneas or very low astigmatism, where a standard lens could still provide excellent vision. A personalised assessment is essential to determine if a toric lens will deliver meaningful benefits in your specific case.
5. What are the main advantages of choosing a toric lens for mild astigmatism?
The primary advantage is improved visual clarity across distances, especially for patients aiming to reduce their reliance on glasses. Toric lenses help eliminate subtle blur or ghosting caused by astigmatism, enhance contrast, and improve night-time vision. They also provide more consistent focus for tasks like reading, computer use, or screen viewing, offering a smoother visual experience overall.
6. How precise are modern toric lenses?
Modern toric lenses are highly advanced and engineered for stability and precision. They feature improved haptic designs that keep the lens securely in place, resisting rotation that could reduce effectiveness. Combined with precise surgical alignment tools, these lenses provide predictable outcomes and long-term visual improvement, making them a reliable choice even for mild astigmatism.
7. Can glasses or laser treatment replace toric lenses after cataract surgery?
Glasses or laser enhancement can correct residual astigmatism, but they require ongoing management and may not offer the same convenience. Toric lenses address astigmatism directly during cataract surgery, providing a long-term solution. For those seeking minimal dependence on glasses, toric lenses usually offer the most efficient and predictable way to achieve clear, stable vision.
8. What happens if mild astigmatism is left uncorrected?
Leaving mild astigmatism uncorrected after cataract surgery generally still results in improved vision, but some issues may persist. Patients may notice residual blur, reduced sharpness, or slight ghosting, especially at night or when viewing distant objects. Dependence on glasses may remain for certain activities, and fine details may not appear as crisp as they could with toric correction.
9. Does choosing a toric lens make a significant financial difference?
Toric lenses are considered premium lenses and do come at an additional cost compared to standard options. Many patients find the investment worthwhile due to the improved visual clarity, comfort, and reduced need for glasses. However, if glasses are not a concern or visual expectations are moderate, a standard lens may still provide excellent results, making the decision largely dependent on personal priorities and lifestyle.
10. How do toric lenses fit into an overall cataract strategy?
Toric lenses are part of a broader approach to optimising post-surgery vision. They specifically target astigmatism while complementing other lens choices, such as blended vision, monovision, or enhanced intermediate correction. Surgeons consider each patient’s lifestyle, eye measurements, and long-term goals to create a personalised plan, ensuring the clearest and most functional vision possible after surgery.
Final Thought: Toric Lenses for Mild Astigmatism
Toric lenses can play a key role in achieving sharper, more comfortable vision after cataract surgery, even for patients with mild astigmatism. By addressing subtle distortions and reducing reliance on glasses, they often provide long-term benefits that improve both clarity and quality of life. Choosing the right lens, however, requires a personalised assessment of your eye measurements, lifestyle, and visual goals. If you’re looking for toric lenses in London, you can book a consultation with our specialist at the London Cataract Centre to discuss your options and find the lens that best suits your needs.
References:
1. Nemet, A.Y., et al. (2025) Clinical Outcomes Following Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation in Cataract Patients with Corneal Astigmatism, Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(7), p.2316. https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/14/7/2316
2. Ichikawa, K., et al. (2025) Study on Factors Affecting Toric Intraocular Lens Rotation in Cataract Surgery, Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(18). https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/14/18/6599
3. Kessel, L., Hjortdal, J. and Zetterström, C. (2016) Toric Intraocular Lenses in the Correction of Astigmatism During Cataract Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta‑Analysis, Ophthalmology, 123(2), pp.275–286. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26601819/
4. Goggin, M., et al. (2022) Toric Intraocular Lenses: Evidence‑Based Use for Astigmatism Correction, British Journal of Ophthalmology (review) provides clinical context for selecting toric IOLs and predicting visual outcomes in astigmatism correction. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9543206/
5. Tang, Q., et al. (2025) Comparative Analysis of Three Toric Intraocular Lenses: Visual and Refractive Outcomes, Journal of Cataract & Refractive Surgery compares performance of different toric IOL models in visual outcomes and refractive results at 3‑month follow‑up. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266737622500054X